- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Glutaredoxin-1 alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury by decreasing its toxic metabolites

Read this article at
Abstract
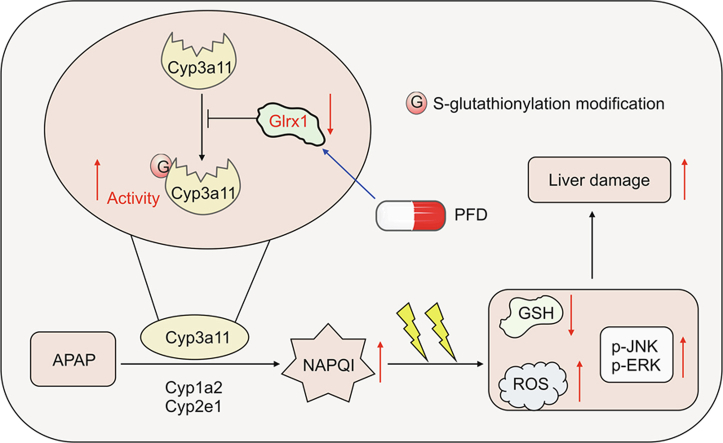
Excessive N-acetyl- p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) formation is a starting event that triggers oxidative stress and subsequent hepatocyte necrosis in acetaminophen (APAP) overdose caused acute liver failure (ALF). S-glutathionylation is a reversible redox post-translational modification and a prospective mechanism of APAP hepatotoxicity. Glutaredoxin-1 (Glrx1), a glutathione-specific thioltransferase, is a primary enzyme to catalyze deglutathionylation. The objective of this study was to explored whether and how Glrx1 is associated with the development of ALF induced by APAP. The Glrx1 knockout mice ( Glrx1 −/− ) and liver-specific overexpression of Glrx1 ( AAV8-Glrx1) mice were produced and underwent APAP-induced ALF. Pirfenidone (PFD), a potential inducer of Glrx1, was administrated preceding APAP to assess its protective effects. Our results revealed that the hepatic total protein S-glutathionylation (PSSG) increased and the Glrx1 level reduced in mice after APAP toxicity. Glrx1 −/− mice were more sensitive to APAP overdose, with higher oxidative stress and more toxic metabolites of APAP. This was attributed to Glrx1 deficiency increasing the total hepatic PSSG and the S-glutathionylation of cytochrome p450 3a11 (Cyp3a11), which likely increased the activity of Cyp3a11. Conversely, AAV8-Glrx1 mice were defended against liver damage caused by APAP overdose by inhibiting the S-glutathionylation and activity of Cyp3a11, which reduced the toxic metabolites of APAP and oxidative stress. PFD precede administration upregulated Glrx1 expression and alleviated APAP-induced ALF by decreasing oxidative stress. We have identified the function of Glrx1 mediated PSSG in liver injury caused by APAP overdose. Increasing Glrx1 expression may be investigated for the medical treatment of APAP-caused hepatic injury.
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Glrx-1 deficiency increases NAPQI and aggravates APAP-induced hepatotoxicity.
-
•
Glrx-1 deficiency increases the S-glutathionylation of Cyp3a11 and its activity.
-
•
Glrx-1 overexpression decreases NAPQI formation and APAP hepatotoxicity.
-
•
PFD alleviates APAP hepatotoxicity by inducing Glrx1 expression and reducing ROS.
Related collections
Most cited references48

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity: a Comprehensive Update
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found