- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ligusticum chuanxiong promotes the angiogenesis of preovulatory follicles (F1–F3) in late-phase laying hens

Read this article at
Abstract
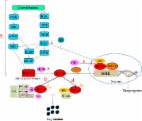
Ligusticum chuanxiong ( CX) is a traditional Chinese medicine that is widely planted throughout the world. CX is one of the most important and commonly used drugs to enhance blood circulation. The preovulatory follicles in laying hens have a large number of blood arteries and meridians that feed the follicles’ growth and maturation with nutrients, hormones, and cytokines. With the extension of laying time, preovulatory follicles angiogenesis decreased gradually. In this study, we studied the mechanism of CX on preovulatory follicles angiogenesis in late-phase laying hens. The results show that CX extract can increase the angiogenesis of preovulatory follicles (F1–F3) of late-phase laying hens. CX extract can promote vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 ( VEGFR2) phosphorylation in preovulatory follicles theca layers, promote the proliferation, invasion and migration through PI3K/AKT and RAS/ERK signaling pathways in primary follicle microvascular endothelial-like cells ( FMECs). In addition, CX extract can up-regulate the expression of hypoxia inducible factor α ( HIF1α) in granulosa cells ( GCs) and granulosa layers through PI3K/AKT and RAS/ERK signaling pathways, thereby promoting the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor A ( VEGFA). In conclusion, the current study confirmed the promoting effect of CX extract on the preovulatory follicles angiogenesis, which sets the stage for the design of functional animal feed for late-phase laying hens.
Related collections
Most cited references63
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found