- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Molecular diversity of Pseudoscorpiones in southern High Appalachian leaf litter

Read this article at
Abstract
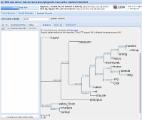
The Pseudoscorpiones fauna of North America is diverse, but in regions like the southern Appalachian Mountains, they are still poorly documented with respect to their species diversity, distributions and ecology. Several families have been reported from these mountains and neighbouring areas. Here we analyse barcoding data of 136 specimens collected in leaf litter, most of them from high-elevation coniferous forest. We used ASAP as a species delimitation method to obtain an estimation of the number of species present in the region. For this and based on interspecific genetic distance values previously reported in Pseudoscorpions, we considered three different genetic Kimura two-parameter distance thresholds (3%/5%/8%), to produce more or less conservative estimates. These distance thresholds resulted in 64/47/27 distinct potential species representing the families Chthoniidae (33/22/12 species) and Neobisiidae (31/25/15) and at least six different genera within them. The diversity pattern seems to be affected by the Asheville Depression, a major biogeographic barrier in this area, with a higher diversity to the west of this geographic feature, particularly within the family Neobisiidae . The absence of representatives from other families amongst our studied samples may be explained by differences in their ecological requirements and occupation of different microhabitats.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found