- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Transcriptome analysis of rice root heterosis by RNA-Seq
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Heterosis is a phenomenon in which hybrids exhibit superior performance relative to parental phenotypes. In addition to the heterosis of above-ground agronomic traits on which most existing studies have focused, root heterosis is also an indispensable component of heterosis in the entire plant and of major importance to plant breeding. Consequently, systematic investigations of root heterosis, particularly in reproductive-stage rice, are needed. The recent advent of RNA sequencing technology (RNA-Seq) provides an opportunity to conduct in-depth transcript profiling for heterosis studies.
Results
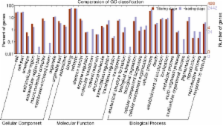
Using the Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform, the root transcriptomes of the super-hybrid rice variety Xieyou 9308 and its parents were analyzed at tillering and heading stages. Approximately 391 million high-quality paired-end reads (100-bp in size) were generated and aligned against the Nipponbare reference genome. We found that 38,872 of 42,081 (92.4%) annotated transcripts were represented by at least one sequence read. A total of 829 and 4186 transcripts that were differentially expressed between the hybrid and its parents (DG HP) were identified at tillering and heading stages, respectively. Out of the DG HP, 66.59% were down-regulated at the tillering stage and 64.41% were up-regulated at the heading stage. At the heading stage, the DG HP were significantly enriched in pathways related to processes such as carbohydrate metabolism and plant hormone signal transduction, with most of the key genes that are involved in the two pathways being up-regulated in the hybrid. Several significant DG HP that could be mapped to quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for yield and root traits are also involved in carbohydrate metabolism and plant hormone signal transduction pathways.
Conclusions
An extensive transcriptome dataset was obtained by RNA-Seq, giving a comprehensive overview of the root transcriptomes at tillering and heading stages in a heterotic rice cross and providing a useful resource for the rice research community. Using comparative transcriptome analysis, we detected DG HP and identified a group of potential candidate transcripts. The changes in the expression of the candidate transcripts may lay a foundation for future studies on molecular mechanisms underlying root heterosis.
Related collections
Most cited references62
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Deep RNA sequencing at single base-pair resolution reveals high complexity of the rice transcriptome.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found