- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children based on WHO clinical guidelines
Read this article at
Abstract
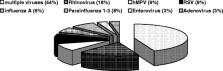
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a major cause of death in developing countries and of morbidity in developed countries. The objective of the study was to define the causative agents among children hospitalized for CAP defined by WHO guidelines and to correlate etiology with clinical severity and surrogate markers. Investigations included an extensive etiological workup. A potential causative agent was detected in 86% of the 99 enrolled patients, with evidence of bacterial (53%), viral (67%), and mixed (33%) infections. Streptococcus pneumoniae was accounted for in 46% of CAP. Dehydration was the only clinical sign associated with bacterial pneumonia. CRP and PCT were significantly higher in bacterial infections. Increasing the number of diagnostic tests identifies potential causes of CAP in up to 86% of children, indicating a high prevalence of viruses and frequent co-infections. The high proportion of pneumococcal infections re-emphasizes the importance of pneumococcal immunization.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Evaluation and improvement of real-time PCR assays targeting lytA, ply, and psaA genes for detection of pneumococcal DNA.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
