- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ecology of Nitrogen Fixing, Nitrifying, and Denitrifying Microorganisms in Tropical Forest Soils
Read this article at
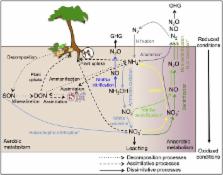
Abstract
Soil microorganisms play important roles in nitrogen cycling within forest ecosystems. Current research has revealed that a wider variety of microorganisms, with unexpected diversity in their functions and phylogenies, are involved in the nitrogen cycle than previously thought, including nitrogen-fixing bacteria, ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea, heterotrophic nitrifying microorganisms, and anammox bacteria, as well as denitrifying bacteria, archaea, and fungi. However, the vast majority of this research has been focused in temperate regions, and relatively little is known regarding the ecology of nitrogen-cycling microorganisms within tropical and subtropical ecosystems. Tropical forests are characterized by relatively high precipitation, low annual temperature fluctuation, high heterogeneity in plant diversity, large amounts of plant litter, and unique soil chemistry. For these reasons, regulation of the nitrogen cycle in tropical forests may be very different from that of temperate ecosystems. This is of great importance because of growing concerns regarding the effect of land use change and chronic-elevated nitrogen deposition on nitrogen-cycling processes in tropical forests. In the context of global change, it is crucial to understand how environmental factors and land use changes in tropical ecosystems influence the composition, abundance and activity of key players in the nitrogen cycle. In this review, we synthesize the limited currently available information regarding the microbial communities involved in nitrogen fixation, nitrification and denitrification, to provide deeper insight into the mechanisms regulating nitrogen cycling in tropical forest ecosystems. We also highlight the large gaps in our understanding of microbially mediated nitrogen processes in tropical forest soils and identify important areas for future research.
Related collections
Most cited references201
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found