- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Promoter of the pri-miR-375 Gene Directs Expression Selectively to the Endocrine Pancreas
Abstract
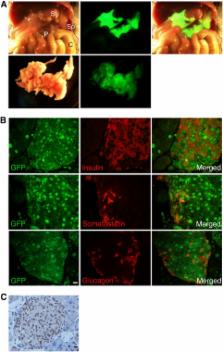
microRNAs (miRNAs) are known to play an essential role in controlling a broad range of biological processes including animal development. Accordingly, many miRNAs are expressed preferentially in one or a small number of cell types. Yet the mechanisms responsible for this selectivity are not well understood. The aim of this study was to elucidate the molecular basis of cell-specific expression of the pri-miR-375 gene, which is selectively expressed in pancreatic islets, and has been implicated both in the development of islets, and the function of mature pancreatic beta cells. An evolutionarily conserved 768 bp region of DNA upstream of the pri-miR-375 gene was linked to GFP and luciferase reporter genes, and expression monitored in transgenic mice and transfected cultured cells. Deletion and targeted mutagenesis analysis was used to evaluate the functional significance of sequence blocks within the upstream fragment. 5′-RACE analysis was used for mapping the pri-miR-375 gene transcription start site. The conserved 768 bp region was able to direct preferential expression of a GFP reporter gene to pancreatic islets in transgenic mice. Deletion analysis using a luciferase reporter gene in transfected cultured cell lines confirmed the cell specificity of the putative promoter region, and identified several key cis-elements essential for optimal activity, including E-boxes and a TATA sequence. Consistent with this, 5′-RACE analysis identified a transcription start site within this DNA region, 24 bp downstream of the TATA sequence. These studies define the promoter of the pri-miR-375 gene, and show that islet-specific expression of the pri-miR-375 gene is controlled at the transcriptional level. Detailed analysis of the transcriptional mechanisms controlling expression of miRNA genes will be essential to permit a comprehensive understanding of the complex role of miRNAs such as miR-375 in developmental processes.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Dicer is essential for mouse development.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Selective blockade of microRNA processing by Lin28.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to p53-mediated apoptosis.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.