- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Species diversity and major host/substrate associations of the genus Akanthomyces (Hypocreales, Cordycipitaceae)
Read this article at
Abstract
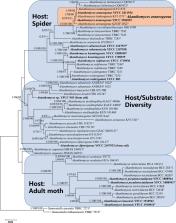
Akanthomyces , a group of fungi with rich morphological and ecological diversity in Cordycipitaceae ( Ascomycota , Hypocreales ), has a wide distribution amongst diverse habitats. By surveying arthropod-pathogenic fungi in China and Southeast Asia over the last six years, nine Akanthomyces spp. were found and identified. Five of these were shown to represent four known species and an undetermined species of Akanthomyces . Four of these were new species and they were named A. kunmingensis and A. subaraneicola from China, A. laosensis from Laos and A. pseudonoctuidarum from Thailand. The new species were described and illustrated according to the morphological characteristics and molecular data. Akanthomyces araneogenus , which was isolated from spiders from different regions in China, Thailand and Vietnam, was described as a newly-recorded species from Thailand and Vietnam. The phylogenetic positions of the nine species were evaluated, based on phylogenetic inferences according to five loci, namely, ITS, nrLSU, TEF, RPB1 and RPB2. In this study, we reviewed the research progress achieved for Akanthomyces regarding its taxonomy, species diversity, geographic distribution and major host/substrate associations. The morphological characteristics of 35 species in Akanthomyces , including four novel species and 31 known taxa, were also compared.
Related collections
Most cited references55
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice Across a Large Model Space
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found