- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Evaluation of Metformin Hydrochloride Tailoring Bilosomes as an Effective Transdermal Nanocarrier
Abstract
Introduction
Metformin hydrochloride (metformin HCL), a first-line drug treating diabetes type II, was known to cause severe gastritis, so seeking a non-oral dosage form was the new trend. Bilosomes are bilayer nano-vesicles of non-ionic surfactants embodying bile salts. In our study, bilosomes were investigated as an acceptable novel carrier for active targeting transdermal delivery of metformin HCL, circumventing its side effects.
Methods
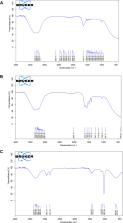
Twelve bilosome formulations were prepared with solvent evaporation method with slight modification according to a 3 1.2 2 full factorial design, and the optimized formulation was determined using Design -Expert 13 software (Stat-Ease, Inc., Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA) studying the effect of surfactant and bile salt types on the entrapment efficiency (EE), vesicle size (VS), polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential (ZP), percentage of drug released within 24 h (R), and flux of drug permeated within 6 h (Jss) of vesicles. In addition, the optimized formulation was further evaluated to Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), deformability index (DI), and transmission electron microscope (TEM) to ensure bilosomes formation, elasticity, and spherical shape, respectively.
Results
The resulting vesicles publicized EE from 56.21% to 94.21%, VS from 183.64 to 701.8 nm, PDI values oscillating between 0.33 and 0.53, ZP (absolute value) from 29 to 44.2 mV, biphasic release profile within 24 h from 60.62 and up to 75.28%, and permeation flux enhancement (198.79–431.91 ng cm −2 h −1) in comparison with the non-formulated drug (154.26 ng cm −2 h −1). Optimized formulation was found to be F8 with EE = 79.49%, VS = 237.68 nm, ZP = 40.9 mV, PDI = 0.325, R = 75.28%, Jss = 333.45 ng cm −2 h −1 and DI = 6.5 with spherical self-closed non-aggregated vesicles and non-superimposed bands of its components in the FTIR.
Video abstract
Point your SmartPhone at the code above. If you have a QR code reader the video abstract will appear. Or use:
Graphical Abstract
Most cited references54
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Natural skin surface pH is on average below 5, which is beneficial for its resident flora.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Role of edge activators and surface charge in developing ultradeformable vesicles with enhanced skin delivery.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found

