- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Pharmacological Basis for Use of a Novel Compound in Hyperuricemia: Anti-Hyperuricemic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Read this article at
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of hyperuricemia is considered high worldwide. Hyperuricemia occurs due to decreased excretion of uric acid, increased synthesis of uric acid, or a combination of both mechanisms. There is growing evidence that hyperuricemia is associated with a decline of renal function.
Purpose: This study is aimed at investigating the effects of the novel compound on lowering the serum uric acid level and alleviating renal inflammation induced by high uric acid in hyperuricemic mice.
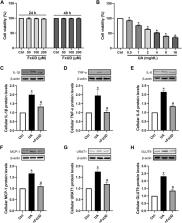
Methods: Hyperuricemic mice model was induced by potassium oxonate and used to evaluate the effects of the novel compound named FxUD. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect the related biochemical markers. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining was applied to observe pathological changes. The mRNA expression levels were tested by qRT-PCR. The protein levels were determined by Western blot. In parallel, human proximal renal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2) derived from normal kidney was used to further validate the anti-inflammatory effects in vitro.
Results: FxUD administration significantly decreased serum uric acid levels, restored the kidney function parameters, and improved the renal pathological injury. Meanwhile, treatment with FxUD effectively inhibited serum and liver xanthine oxidase (XOD) levels. Reversed expression alterations of renal inflammatory cytokines, urate transporter 1 (URAT1) and glucose transporter 9 (GLUT9) were observed in hyperuricemic mice. Western blot results illustrated FxUD down-regulated protein levels of inflammasome components. Further studies showed that FxUD inhibited the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway in the kidney of hyperuricemic mice. In parallel, the anti-inflammatory effect of FxUD was also confirmed in HK-2.
Conclusion: Our study reveals that FxUD exhibits the anti-hyperuricemic and anti-inflammatory effects through regulating hepatic XOD and renal urate reabsorption transporters, and suppressing NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway in hyperuricemia. The results provide the evidence that FxUD may be potential for the treatment of hyperuricemia with kidney inflammation.
Related collections
Most cited references55
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Origin and physiological roles of inflammation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found