- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Hypoglycemic and antilipidemic properties of kombucha tea in alloxan-induced diabetic rats
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Diabetes has become a serious health problem and a major risk factor associated with troublesome health complications, such as metabolism disorders and liver-kidney dysfunctions. The inadequacies associated with conventional medicines have led to a determined search for alternative natural therapeutic agents. The present study aimed to investigate and compare the hypoglycemic and antilipidemic effects of kombucha and black tea, two natural drinks commonly consumed around the world, in surviving diabetic rats.
Methods
Alloxan diabetic rats were orally supplied with kombucha and black tea at a dose of 5 mL/kg body weight per day for 30 days, fasted overnight, and sacrificed on the 31st day of the experiment. Their bloods were collected and submitted to various biochemical measurements, including blood glucose, cholesterol, triglcerides, urea, creatinine, transaminases, transpeptidase, lipase, and amylase activities. Their pancreases were isolated and processed to measure lipase and α-amylase activities and to perform histological analysis.
Results
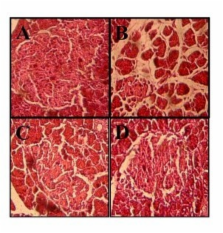
The findings revealed that, compared to black tea, kombucha tea was a better inhibitor of α-amylase and lipase activities in the plasma and pancreas and a better suppressor of increased blood glucose levels. Interestingly, kombucha was noted to induce a marked delay in the absorption of LDL-cholesterol and triglycerides and a significant increase in HDL-cholesterol. Histological analyses also showed that it exerted an ameliorative action on the pancreases and efficiently protected the liver-kidney functions of diabetic rats, evidenced by significant decreases in aspartate transaminase, alanine transaminase, and gamma-glytamyl transpeptidase activities in the plasma, as well as in the creatinine and urea contents.
Conclusions
The findings revealed that kombucha tea administration induced attractive curative effects on diabetic rats, particularly in terms of liver-kidney functions. Kombucha tea can, therefore, be considered as a potential strong candidate for future application as a functional supplement for the treatment and prevention of diabetes.
Related collections
Most cited references48
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Quercetin, a flavonoid antioxidant, prevents and protects streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress and beta-cell damage in rat pancreas.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Anti-diabetic effect of cinnamon extract on blood glucose in db/db mice.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found