- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Pain‐autonomic interaction is a reliable measure of pain habituation in healthy subjects
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Habituation is a response decrement resulting from repeated stimuli. Reduced habituation to noxious stimuli is considered to be a proxy for central sensitization in subjects with chronic pain. Despite numerous investigations of pain habituation in relation to central sensitization, there is no consensus on the most sensitive and reliable readout, as well as analysis approach. Therefore, this study compared the usability and reliability of different readouts and habituation analysis approaches to measure pain habituation in response to repetitive heat simulation.
Methods
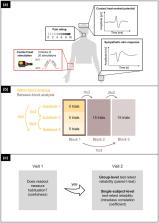
Three blocks of 20 contact heat stimuli were applied on the volar forearm of 20 healthy subjects on two separate visits. Habituation was assessed by three different readouts: pain ratings, contact heat evoked potentials (CHEPs) and heat‐induced sympathetic skin responses (SSRs). In addition, two different habituation analysis approaches were used: between the three stimulation blocks (between‐block) and within the first stimulation block (within‐block).
Results
Significant between‐block habituation for SSRs ( p < 0.001), but not for pain ratings ( p = 1.000) and CHEPs ( p = 0.078) was found. There was significant within‐block habituation for pain ratings ( p = 0.012) and SSRs ( p < 0.001), but not for CHEPs ( p = 0.246). Only the between‐block habituation of heat‐induced SSR was reliable between the two visits (first to second block: intraclass correlation coefficient [ICC] = 0.58, p = 0.030; first to third block: ICC = 0.64, p = 0.015).
Related collections
Most cited references57
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The hospital anxiety and depression scale.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found