- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Electroacupuncture Attenuated Anxiety and Depression-Like Behavior via Inhibition of Hippocampal Inflammatory Response and Metabolic Disorders in TNBS-Induced IBD Rats
Read this article at
Abstract
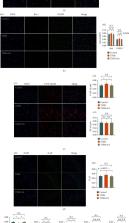
This study was designed to explore the potential mechanisms of electroacupuncture (EA) in treating inflammatory bowel disease- (IBD-) related anxiety and mood disorders. A colitis model was induced in rats with 2, 4, 6-trinitrohydrosulfonic acid (TNBS), followed by ST36 and SP6 targeted therapy by EA or sham EA treatment. The elevated plus maze (EPM) and open-field test (OFT) were performed to assess the state of anxiety and depression-like behavior. Tests were carried out by 16S rDNA amplification sequence, 1H nuclear magnetic resonance ( 1H NMR) spectroscopy, immunofluorescence staining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The analyses detailed metabolic alterations and the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathway/NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in rats' hippocampal region. Furthermore, the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis and gut microbiome was assessed. As a result of treatment, EA significantly improved in the behavioral tests and altered the composition of the gut microbiome through a significant increase in the density of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) producers mainly including Ruminococcaceae, Phascolarctobacterium, and Akkermansiaceae. EA upregulated the metabolites of the hippocampus mainly containing l-glutamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), as well as ZO-1 expression. Whereas the treatment blocked the TLR4/nuclear factor- kappa B (NF- κB) signaling pathways and NLRP3 inflammasomes, along with downregulating the interleukin- (IL-) 1 β level. The hyperactivity of the HPA axis was also diminished. In conclusion, EA at ST36 and SP6 attenuated anxiety and depression-like behavior in colitis model rats through their effects on the gut microbiome by modulating the hippocampal inflammatory response and metabolic disorders, as well as the HPA axis. This study provides evidence for clinical application of EA to serve as an adjunctive treatment for IBD-related anxiety and depression.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found