- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Role of Hippo Pathway-YAP/TAZ Signaling in Angiogenesis
Read this article at
Abstract
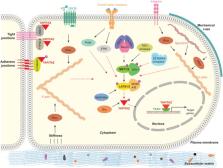
Angiogenesis is a highly coordinated process of formation of new blood vessels from pre-existing blood vessels. The process of development of the proper vascular network is a complex process that is crucial for the vertebrate development. Several studies have defined essential roles of Hippo pathway-YAP/TAZ in organ size control, tissue regeneration, and self-renewal. Thus Hippo pathway is one of the central components in tissue homeostasis. There are mounting evidences on the eminence of Hippo pathway-YAP/TAZ in angiogenesis in multiple model organisms. Hippo pathway-YAP/TAZ is now demonstrated to regulate endothelial cell proliferation, migration and survival; subsequently regulating vascular sprouting, vascular barrier formation, and vascular remodeling. Major intracellular signaling programs that regulate angiogenesis concomitantly activate YAP/TAZ to regulate key events in angiogenesis. In this review, we provide a brief overview of the recent findings in the Hippo pathway and YAP/TAZ signaling in angiogenesis.
Related collections
Most cited references89
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway by G-protein-coupled receptor signaling.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
VEGF as a Key Mediator of Angiogenesis in Cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found