- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Recent Advances and Future Perspectives on Microfluidic Liquid Handling
Read this article at
Abstract
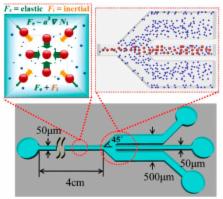
The interdisciplinary research field of microfluidics has the potential to revolutionize current technologies that require the handling of a small amount of fluid, a fast response, low costs and automation. Microfluidic platforms that handle small amounts of liquid have been categorised as continuous-flow microfluidics and digital microfluidics. The first part of this paper discusses the recent advances of the two main and opposing applications of liquid handling in continuous-flow microfluidics: mixing and separation. Mixing and separation are essential steps in most lab-on-a-chip platforms, as sample preparation and detection are required for a variety of biological and chemical assays. The second part discusses the various digital microfluidic strategies, based on droplets and liquid marbles, for the manipulation of discrete microdroplets. More advanced digital microfluidic devices combining electrowetting with other techniques are also introduced. The applications of the emerging field of liquid-marble-based digital microfluidics are also highlighted. Finally, future perspectives on microfluidic liquid handling are discussed.
Related collections
Most cited references135
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found