- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Novel Combination BMP7 and HGF Gene Therapy Instigates Selective Myofibroblast Apoptosis and Reduces Corneal Haze In Vivo
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose
We tested the potential of bone morphogenic protein 7 ( BMP7) and hepatocyte growth factor ( HGF) combination gene therapy to treat preformed corneal fibrosis using established rabbit in vivo and human in vitro models.
Methods
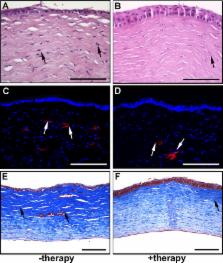
Eighteen New Zealand White rabbits were used. Corneal fibrosis was produced by alkali injury. Twenty-four hours after scar formation, cornea received topically either balanced salt solution (BSS; n = 6), polyethylenimine-conjugated gold nanoparticle (PEI2-GNP)-naked plasmid ( n = 6) or PEI2-GNP plasmids expressing BMP7 and HGF genes ( n = 6). Donor human corneas were used to obtain primary human corneal fibroblasts and myofibroblasts for mechanistic studies. Gene therapy effects on corneal fibrosis and ocular safety were evaluated by slit-lamp microscope, stereo microscopes, quantitative real-time PCR, immunofluorescence, TUNEL, modified MacDonald-Shadduck scoring system, and Draize tests.
Results
PEI2-GNP–mediated BMP7+ HGF gene therapy significantly decreased corneal fibrosis in live rabbits in vivo (Fantes scale was 0.6 in BMP7+ HGF-treated eyes compared to 3.3 in −therapy group; P < 0.001). Corneas that received BMP7+ HGF demonstrated significantly reduced mRNA levels of profibrotic genes: α-SMA (3.2-fold; P < 0.01), fibronectin (2.3-fold, P < 0.01), collagen I (2.1-fold, P < 0.01), collagen III (1.6-fold, P < 0.01), and collagen IV (1.9-fold, P < 0.01) compared to the −therapy corneas. Furthermore, BMP7+ HGF-treated corneas showed significantly fewer myofibroblasts compared to the −therapy controls (83%; P < 0.001). The PEI2-GNP introduced >10 4 gene copies per microgram DNA of BMP7 and HGF genes. The recombinant HGF rendered apoptosis in corneal myofibroblasts but not in fibroblasts. Localized topical BMP7+ HGF therapy showed no ocular toxicity.
Related collections
Most cited references56
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Causes and prevalence of visual impairment among adults in the United States.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Transcriptional control by the TGF-beta/Smad signaling system.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found