- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Attainment of polarity promotes growth factor secretion by retinal pigment epithelial cells: Relevance to age-related macular degeneration
Read this article at
Abstract
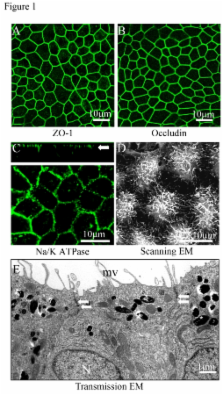
The antiangiogenic and neurotrophic growth factor, pigment epithelial derived factor (PEDF), and the proangiogenic growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF), are released from retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells where they play a critical role in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Since RPE polarity may be altered in advanced AMD, we studied the effect of polarization of differentiated, human RPE monolayer cultures on expression and secretion of PEDF and VEGF. Polarized RPE demonstrated apical microvilli, expression of tight junction proteins, apical localization of Na/K- ATPase, and high transepithelial resistance (490 ± 17 Ω•cm 2). PEDF secretion was about 1000 fold greater than that for VEGF in both polarized and non-polarized cultures. Polarization of the RPE monolayer increased PEDF secretion, which was predominantly apical, by 34 fold (p<0.02) and VEGF secretion, which was predominantly basolateral, by 5.7 fold (p<0.02). Treatment of non-polarized RPE cultures with bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4) had no effect on PEDF or VEGF secretion, but resulted in a dose-dependent >2-fold increase in basolateral VEGF secretion (p<0.05) in polarized cultures. Our data show that polarity is an important determinant of the level of PEDF and VEGF secretion in RPE and support the contention that loss of polarity of RPE in AMD results in marked loss of neurotrophic and vascular support for the retina potentially leading to photoreceptor loss and blindness.
Related collections
Most cited references50
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Increased vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the vitreous of eyes with proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found