- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
FAPI-74 PET/CT Using Either 18F-AlF or Cold-Kit 68Ga Labeling: Biodistribution, Radiation Dosimetry, and Tumor Delineation in Lung Cancer Patients
Read this article at
Abstract
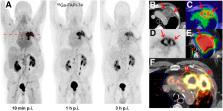
68Ga-fibroblast activation protein inhibitors (FAPIs) 2, 4, and 46 have already been proposed as promising PET tracers. However, the short half-life of 68Ga (68 min) creates problems with manufacture and delivery. 18F (half-life, 110 min) labeling would result in a more practical large-scale production, and a cold-kit formulation would improve the spontaneous availability. The NOTA chelator ligand FAPI-74 can be labeled with both 18F-AlF and 68Ga. Here, we describe the in vivo evaluation of 18F-FAPI-74 and a proof of mechanism for 68Ga-FAPI-74 labeled at ambient temperature. Methods: In 10 patients with lung cancer, PET scans were acquired at 10 min, 1 h, and 3 h after administration of 259 ± 26 MBq of 18F-FAPI-74. Physiologic biodistribution and tumor uptake were semiquantitatively evaluated on the basis of SUV at each time point. Absorbed doses were evaluated using OLINDA/EXM, version 1.1, and QDOSE dosimetry software with the dose calculator IDAC-Dose, version 2.1. Identical methods were used to evaluate one examination after injection of 263 MBq of 68Ga-FAPI-74. Results: The highest contrast was achieved in primary tumors, lymph nodes, and distant metastases at 1 h after injection, with an SUV max of more than 10. The effective dose per a 100-MBq administered activity of 18F-FAPI-74 was 1.4 ± 0.2 mSv, and for 68Ga-FAPI-74 it was 1.6 mSv. Thus, the radiation burden of a diagnostic 18F-FAPI-74 PET scan is even lower than that of PET scans with 18F-FDG and other 18F tracers; 68Ga-FAPI-74 is comparable to other 68Ga ligands. FAPI PET/CT supported target volume definition for guiding radiotherapy. Conclusion: The high contrast and low radiation burden of FAPI-74 PET/CT favor multiple clinical applications. Centralized large-scale production of 18F-FAPI-74 or decentralized cold-kit labeling of 68Ga-FAPI-74 allows flexible routine use.
Related collections
Most cited references44
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Tracer Uptake in 28 Different Kinds of Cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Non-small-cell lung cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found