- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Numerical computation of pulsatile hemodynamics and diagnostic concern of coronary bifurcated artery flow for Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluid
Read this article at
Abstract
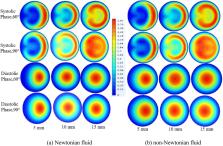
Atherosclerotic with the high occurrence of plaque formation due to stenosis has attracted wide attention among researchers. The left coronary artery has been studied in two-dimensional and in three-dimensional (3D) bifurcation as the models of blood flow through Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids to better understand the physical mechanism. The computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) technique is incorporated in COMSOL Multiphysics and then it is justified by satisfactory validation. It is found that the Newtonian model shows larger recirculation zones than non-Newtonian does. The present study also focuses on the evaluations of the lesion of diagnostic and the coefficient of pressure drop assessments on the basis of the diagnostic parameter’s critical values affected by the rheological model. Nevertheless, the leading concentration of the subsisting investigation works is confined to the change of importance factor affected by arterial blockage. But the IFc of non-Newtonian fluid for 3D left coronary artery bifurcation model decreases with increasing bifurcation angle and the time-averaged inlet pressure is the least for smaller bifurcation angles. The current research further concentrates that the flow separation length reduces with developing bifurcation angle in bifurcated geometry. It is significant to mention that non-Newtonian blood flow model incorporating hemodynamic and diagnostic parameters has great impacts on instantaneous flow systems.
Related collections
Most cited references34
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Non-Newtonian blood flow in human right coronary arteries: steady state simulations.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pulsatile flow in the human left coronary artery bifurcation: average conditions.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found