- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Testing the bipolar assumption of Singer-Loomis Type Deployment Inventory for Korean adults using classification and multidimensional scaling
Read this article at
Abstract
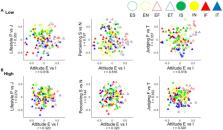
In this study, we explored whether the Korean version of Singer Loomis Type Deployment Inventory II (K-SLTDI) captures the opposing tendencies of Jung’s theory of psychological type. The types are Extroverted Sensing, Extroverted Intuition, Extroverted Feeling, Extroverted Thinking, Introverted Sensing, Introverted Intuition, Introverted Feeling, and Introverted Thinking. A nationwide online survey was conducted in South Korea. We performed multidimensional scaling and classification analyses based on 521 Korean adult profiles with eight psychological types to test the bipolarity assumption. The results showed that the Procrustes-rotated four-dimensional space successfully represented four types of opposing tendencies. Moreover, the bipolarity assumption in the four dimensions of Jungian typology was tested and compared between lower and higher psychological distress populations via cluster analysis. Lastly, we explored patterns of responses in lower and higher psychological distress populations using intersubject correlation. Both similarity analyses and classification results consistently support the theoretical considerations on the conceptualization of Jung’s type in independent order that the types could be derived without bipolar assumption as Singer and Loomis expected in their Type Development Inventory. Limitations in our study include the sample being randomly selected internet users during the COVID−19 pandemic, despite excellence in the use of the internet in the general Korean population.
Related collections
Most cited references111
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Big Data and Machine Learning in Health Care
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found