- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Metatranscriptomic insights on gene expression and regulatory controls in Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis
Read this article at
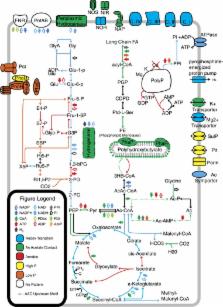
Abstract
Previous studies on enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) have focused on reconstructing genomic blueprints for the model polyphosphate-accumulating organism Candidatus Accumulibacter phosphatis. Here, a time series metatranscriptome generated from enrichment cultures of Accumulibacter was used to gain insight into anerobic/aerobic metabolism and regulatory mechanisms within an EBPR cycle. Co-expressed gene clusters were identified displaying ecologically relevant trends consistent with batch cycle phases. Transcripts displaying increased abundance during anerobic acetate contact were functionally enriched in energy production and conversion, including upregulation of both cytoplasmic and membrane-bound hydrogenases demonstrating the importance of transcriptional regulation to manage energy and electron flux during anerobic acetate contact. We hypothesized and demonstrated hydrogen production after anerobic acetate contact, a previously unknown strategy for Accumulibacter to maintain redox balance. Genes involved in anerobic glycine utilization were identified and phosphorus release after anerobic glycine contact demonstrated, suggesting that Accumulibacter routes diverse carbon sources to acetyl-CoA formation via previously unrecognized pathways. A comparative genomics analysis of sequences upstream of co-expressed genes identified two statistically significant putative regulatory motifs. One palindromic motif was identified upstream of genes involved in PHA synthesis and acetate activation and is hypothesized to be a phaR binding site, hence representing a hypothetical PHA modulon. A second motif was identified ~35 base pairs (bp) upstream of a large and diverse array of genes and hence may represent a sigma factor binding site. This analysis provides a basis and framework for further investigations into Accumulibacter metabolism and the reconstruction of regulatory networks in uncultured organisms.
Related collections
Most cited references46
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Sequencing and comparison of yeast species to identify genes and regulatory elements.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Combining evidence using p-values: application to sequence homology searches.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found