- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effect of artificial or autologous coverage of the pancreatic remnant or anastomosis on postoperative pancreatic fistulas after partial pancreatectomy: meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Postoperative pancreatic fistulas remain a driver of major complications after partial pancreatectomy. It is unclear whether coverage of the anastomosis or pancreatic remnant can reduce the incidence of postoperative pancreatic fistulas. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of autologous or artificial coverage of the pancreatic remnant or anastomosis on outcomes after partial pancreatectomy.
Methods
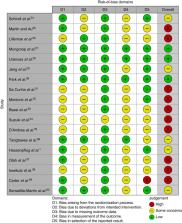
A systematic literature search was performed using MEDLINE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) up to March 2024. All RCTs analysing a coverage method in patients undergoing partial pancreatoduodenectomy or distal pancreatectomy were included. The primary outcome was postoperative pancreatic fistula development. Subgroup analyses for pancreatoduodenectomy or distal pancreatectomy and artificial or autologous coverage were conducted.
Results
A total of 18 RCTs with 2326 patients were included. In the overall analysis, coverage decreased the incidence of postoperative pancreatic fistulas by 29% (OR 0.71, 95% c.i. 0.54 to 0.93, P < 0.01). This decrease was also seen in the 12 RCTs covering the remnant after distal pancreatectomy (OR 0.69, 95% c.i. 0.51 to 0.94, P < 0.02) and the 4 RCTs applying autologous coverage after pancreatoduodenectomy and distal pancreatectomy (OR 0.53, 95% c.i. 0.29 to 0.96, P < 0.04). Other subgroup analyses (artificial coverage or pancreatoduodenectomy) showed no statistically significant differences. The secondary endpoints of mortality, reoperations, and re-interventions were each affected positively by the use of coverage techniques. The certainty of evidence was very low to moderate.
Abstract
Postoperative pancreatic fistulas remain the major complication after partial pancreatectomy. All RCTs investigating the potential benefits of artificial or autologous coverage after partial pancreatectomy were analysed. Coverage techniques as a whole, but especially performed in distal pancreatectomy and the application of autologous material, reduce the incidence of postoperative pancreatic fistulas and mitigate their postoperative burden.
Related collections
Most cited references52

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found