- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
In Search of the Most Stable Molecular Configuration of Heptakis(2,6- O-dimethyl)-β-cyclodextrin and Its Complex with Mianserin: A Comparison of the B3LYP-GD2 and M062X-GD3 Results
Read this article at
Abstract
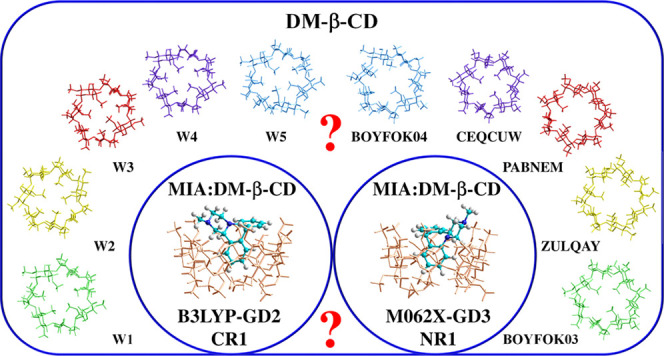
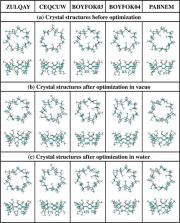
Cyclodextrins are well known for their ability to form stable, highly soluble complexes with various substances, which makes them widely used as excipients in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. In this work, properties of heptakis(2,6- O-dimethyl)-β-cyclodextrin (DM-β-CD) in vacuo and in water, as well as its ability to bind the antidepressant drug mianserin (MIA) in aqueous solution, are investigated computationally. The results are shown to depend strongly on the density functional theory (DFT) applied. The most stable conformers of DM-β-CD found with the B3LYP-GD2 method differ from these indicated by M062X-GD3 and other functionals. According to the latter, two crystal structures, ZULQAY and BOYFOK03, optimized in vacuo and in water, respectively, have the lowest energy. Both the B3LYP-GD2 and M062X-GD3 results show that all tested inclusion and noninclusion complexes of MIA:DM-β-CD in stoichiometry 1:1 are stable in water. However, the structures and their energetic properties obtained with each method differ: in the most stable configurations, different aromatic rings of MIA are embedded inside DM-β-CD, and the corresponding complexation energies (calculated with the 6-31++G(d,p) basis set and corrected for the basis set superposition error) are −29.6 (B3LYP-GD2) and −23.9 (M062X-GD3) kcal/mol. The NMR spectra of DM-β-CD and MIA:DM-β-CD are also compared.
Related collections
Most cited references65
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found