- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Population Based Outcomes of Cataract Surgery in Three Tribal Areas of Andhra Pradesh, India: Risk Factors for Poor Outcomes
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose
To report visual outcomes and risk factors for poor outcomes of cataract surgery in three Integrated Tribal Development Agency (ITDA) areas of Andhra Pradesh, India.
Methods and Results
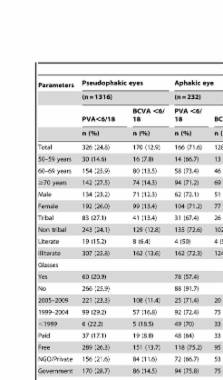
Using validated Rapid Assessment of Avoidable Blindness (RAAB) methodology, a population based cross-sectional study, was conducted in three ITDA areas. A two-stage sampling procedure was used to select 7281 participants aged 50 years and above. Vision assessment using a tumbling E chart and standard ocular examinations were completed. Visual outcomes and risk factors for poor outcomes were assessed among subjects undergoing cataract surgery (1548 eyes of 1124 subjects). Mean age at surgery was 67±8 years; Among the operated eyes, presenting visual acuity (PVA) and best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) worse than 6/18 was seen in 492 (31.8%; 95% CI, 29.5–34.2%) and 298 eyes (19.3%; 95% CI, 17.3–21.3%), respectively. Similarly, PVA and BCVA worse than 6/60 was seen in 219 (14.1%; 95% CI, 12.4–16%) and 147 eyes (9.5%; 95% CI, 8.1–11.1%), respectively. When either eye was taken into consideration, the PVA and BCVA worse than 6/18 was seen in 323 (20.1%; 95% CI, 18.9–23%) and 144 subjects (9.3%; 95% CI, 7.9–10.9%), respectively. PVA and BCVA worse than 6/60 was seen in 74 (4.8%; 95% CI, 3.8–6%) and 49 subjects (3.2%; 95% CI, 2.4–4.2%), respectively. Posterior capsular opacification was seen in 51 of 1316 pseudophakic eyes (3.9%; 95% CI, 2.9–5.1%). In multivariable analysis among pseudophakic subjects with PVA worse than 6/18, increasing age (p = 0.002) and undergoing free surgery (p = 0.05) were independent risk factors. Undergoing surgery before 2005 (p = 0.05) and being illiterate (p = 0.05) were independent risk factors for BCVA worse than 6/18.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Longitudinal data analysis for discrete and continuous outcomes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A population based eye survey of older adults in Tirunelveli district of south India: blindness, cataract surgery, and visual outcomes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found