- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Fabrication of slag/CKD one-mix geopolymer cement reinforced by low-cost nano-particles, mechanical behavior and durability performance
Read this article at
Abstract
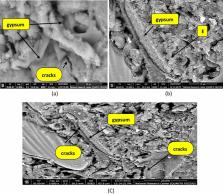
CKD is a byproduct of the cement industry, and its accumulation in the surrounding represents one of many issues associated with this industry. In this study, CKD was utilized in the fabrication of one-mix geopolymer cement (GP) composite as an economical and environmental solution for disposal of this byproduct. The mechanical properties and durability behavior during various deterioration actions were inspected. The obtained findings demonstrated that, replacing slag by CKD in the fabricated GP could cause an elongation in the setting times and reduction in the compression strength of approximately 50%. However, GPs containing CKD offered an accepted resistance to irradiation by γ-rays and to firing action. Reinforcing the GPs with nano Fe 3O 4 (NF) or nano TiO 2 (NT) accelerated the geopolymerization reaction and offered mechanical properties surprising the control mix, this was related to the micro-filling and catalytic actions of the NPs which supported the formation of symmetrical and organized clusters of CSHs and CASH gel as shown in SEM micrographs. The reinforcing mixes surpassing the control mix in the protection against intrusion of sulfate ions which they could retain about 92% of their strength after 4 months of exposure while the control mix retained 80%. Furthermore, they showed a superior resistance to the destructive effect of irradiation by high dose gamma rays up to 1500 kGy and they retained ~ 75% of their strength after irradiation while the control mix was kept at only 35%. The fabricated composites are recommended for usage in many applied construction fields.
Related collections
Most cited references80
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Geopolymer technology: the current state of the art
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2-e) emissions: A comparison between geopolymer and OPC cement concrete
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found