- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Surgical outcomes of concomitantly performed penetrating keratoplasty with intrascleral haptic fixation
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose:
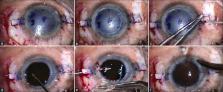
To describe the surgical results of concomitantly performed optical penetrating keratoplasty (PKP) with glued intrascleral haptic fixation (ISHF).
Methods:
Retrospective review of 18 patients (15–72 years) with best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) of ≤1/60 subjected to unilateral concomitant optical PKP with ISHF and followed up for 13.11 ± 5.83 months (6–26 months) was undertaken.
Results:
The most common diagnoses were failed PKP (9/18, 50%) followed by aphakic bullous keratopathy (5/18, 27%). Preoperative glaucoma, peripheral anterior synechiae (PAS), and deep vascularization were present in 7/18 (38.88%), 12/18 (61.11%), and 5/18 (27.77%) patients, respectively. Intraoperatively, concomitant procedures such as pupilloplasty and intraocular lens explant were undertaken in 5/18 (27.277%) patients and 1/18 patients (5.55%) experienced suprachoroidal hemorrhage. At final follow-up, BCVA was ≥6/60 in 50% patients (mean astigmatism: 4.79 ± 1.68D), and 55.55% cases experienced graft failure (90% failed within one year of surgery). The most common causes of graft failure were glaucoma (50%), glaucoma with rejection (20%), rejection (10%), retinal detachment (10%), and suprachoroidal hemorrhage (10%). The ODDS ratio (OR) of having graft failure with the following factors was postoperative secondary interventions (OR: 6), postoperative complications (OR: 2.25), prior failed graft (OR: 1.8), preoperative PAS (OR: 1.75), intraoperative concomitant procedures (OR: 1.5), preoperative glaucoma (OR: 1.33), previous surgeries (OR: 1.24), and deep corneal vessels (OR: 0.66).
Conclusion:
All patients underlying PKP combined with glued ISHF must be counseled about suboptimal surgical outcomes. Emphasis is laid on appropriate case selection and stringent follow-up during the first year after surgery. Secondary interventions should be undertaken cautiously and judiciously in these patients.
Related collections
Most cited references15
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fibrin glue-assisted sutureless posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation in eyes with deficient posterior capsules.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Intermediate results of sutureless intrascleral posterior chamber intraocular lens fixation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found