- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The important role of biochemical and functional studies in the diagnostics of peroxisomal disorders
Read this article at
Abstract
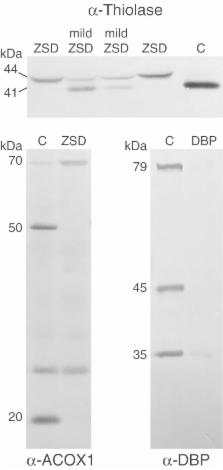
Peroxisomes are dynamic organelles that play an essential role in a variety of metabolic pathways. Peroxisomal dysfunction can lead to various biochemical abnormalities and result in abnormal metabolite levels, such as increased very long-chain fatty acid or reduced plasmalogen levels. The metabolite abnormalities in peroxisomal disorders are used in the diagnostics of these disorders. In this paper we discuss in detail the different diagnostic tests available for peroxisomal disorders and focus specifically on the important role of biochemical and functional studies in cultured skin fibroblasts in reaching the right diagnosis. Several examples are shown to underline the power of such studies.
Related collections
Most cited references56
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Peroxisome biogenesis disorders.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Functions and biosynthesis of plasmalogens in health and disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found