- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Fundus Autofluorescence in Lamellar Macular Holes and Pseudoholes: A Review
Read this article at
Abstract
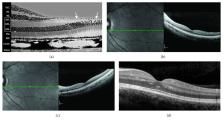
Macular pseudoholes (MPHs) and lamellar macular holes (LMHs) have been recently defined according to spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) criteria. A major feature for differentiating an MPH from an LMH remains the loss of foveal tissue. The anatomy of the foveola is peculiar with the macular pigment (MP) embedded in a very thin layer of tissue underlying the internal limiting membrane and mainly constituted of a specialized group of Müller cells and Henle's fibers. Despite the near microscopic resolution (≈5–7 μm) and the capability to visualize the outer retina in detail, SD-OCT may fail to ascertain whether a very small loss of this foveolar tissue has occurred. Blue-fundus autofluorescence (B-FAF) imaging is useful in this respect because even very small loss of MP can be identified, suggesting a corresponding localized loss of the innermost layers of the foveola. A definition of MP loss would help differentiating an LMH from an MPH where B-FAF imaging will be negative.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The International Vitreomacular Traction Study Group classification of vitreomacular adhesion, traction, and macular hole.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Proposed lexicon for anatomic landmarks in normal posterior segment spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: the IN•OCT consensus.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found