- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Translational impacts of enzymes that modify ribosomal RNA around the peptidyl transferase centre

Read this article at
ABSTRACT
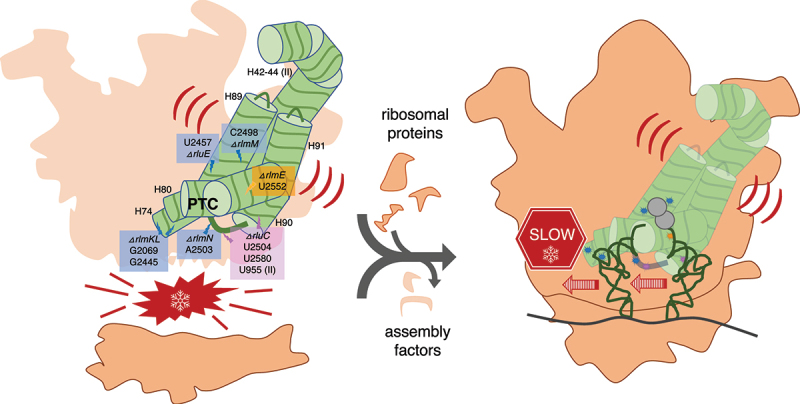
Large ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) are modified heavily post-transcriptionally in functionally important regions but, paradoxically, individual knockouts (KOs) of the modification enzymes have minimal impact on Escherichia coli growth. Furthermore, we recently constructed a strain with combined KOs of five modification enzymes (RluC, RlmKL, RlmN, RlmM and RluE) of the ‘critical region’ of the peptidyl transferase centre (PTC) in 23S rRNA that exhibited only a minor growth defect at 37°C (although major at 20°C). However, our combined KO of modification enzymes RluC and RlmE (not RluE) resulted in conditional lethality (at 20°C). Although the growth rates for both multiple-KO strains were characterized, the molecular explanations for such deficits remain unclear. Here, we pinpoint biochemical defects in these strains. In vitro fast kinetics at 20°C and 37°C with ribosomes purified from both strains revealed, counterintuitively, the slowing of translocation, not peptide bond formation or peptidyl release. Elongation rates of protein synthesis in vivo, as judged by the kinetics of β-galactosidase induction, were also slowed. For the five-KO strain, the biggest deficit at 37°C was in 70S ribosome assembly, as judged by a dominant 50S peak in ribosome sucrose gradient profiles at 5 mM Mg 2+. Reconstitution of this 50S subunit from purified five-KO rRNA and ribosomal proteins supported a direct role in ribosome biogenesis of the PTC region modifications per se, rather than of the modification enzymes. These results clarify the importance and roles of the enigmatic rRNA modifications.
Graphical Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references41

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways. 2017 update
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Book: not found
Experiments in Molecular Genetics
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found