- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Toward systematic review automation: a practical guide to using machine learning tools in research synthesis
Read this article at
Abstract
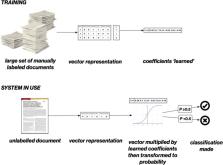
Technologies and methods to speed up the production of systematic reviews by reducing the manual labour involved have recently emerged. Automation has been proposed or used to expedite most steps of the systematic review process, including search, screening, and data extraction. However, how these technologies work in practice and when (and when not) to use them is often not clear to practitioners. In this practical guide, we provide an overview of current machine learning methods that have been proposed to expedite evidence synthesis. We also offer guidance on which of these are ready for use, their strengths and weaknesses, and how a systematic review team might go about using them in practice.
Related collections
Most cited references28
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Conference Proceedings: not found
Neural Architectures for Named Entity Recognition
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Conference Proceedings: not found