- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Experimental Differentiation of Intraocular Masses Using Ultrahigh-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging – A Case Series
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose
The case reports presented here were compiled to demonstrate the potential for improved diagnosis and monitoring of disease progress of intraocular lesions using ultrahigh-field magnetic resonance microscopy (MRM) at 7.1 Tesla.
Methods
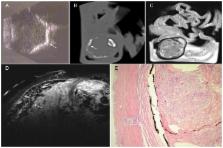
High-resolution ex vivo ocular magnetic resonance (MR) images were acquired on an ultrahigh-field MR system (7.1 Tesla, ClinScan, Bruker BioScan, Germany) using a 2-channel coil with 4 coil elements and T2-weighted turbo spin echo (TSE) sequences of human eyes enucleated because of different intraocular lesions. Imaging parameters were: 40×40 mm field of view, 512×512 matrix, and 700 µm slice thickness. The results were correlated with in vivo ultrasound and histology of the enucleated eyes.
Results
Imaging was performed in enucleated eyes with choroidal melanoma, malignant melanoma of iris and ciliary body with scleral perforation, ciliary body melanoma, intraocular metastasis of esophageal cancer, subretinal bleeding in the presence of perforated corneal ulcer, hemorrhagic choroidal detachment, and premature retinopathy with phthisis and ossification of bulbar structures. MR imaging allowed differentiation between solid and cystic tumor components. In case of hemorrhage, fluid-fluid levels were identified. Melanin and calcifications caused significant hypointensity. Microstructural features of eye lesions identified by MRM were confirmed by histology.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the potential of MRM for the visualization and differential diagnosis of intraocular lesions. At present, the narrow bore of the magnet still limits the use of this technology in humans in vivo. Further advances in ultrahigh-field MR imaging will permit visualization of tumor extent and evaluation of nonclassified intraocular structures in the near future.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Choroidal thickness in Behcet's uveitis: an enhanced depth imaging-optical coherence tomography and its association with angiographic changes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found