- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Phage selection restores antibiotic sensitivity in MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Read this article at
Abstract
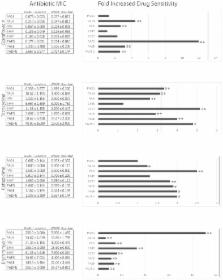
Increasing prevalence and severity of multi-drug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections has necessitated novel antibacterial strategies. Ideally, new approaches would target bacterial pathogens while exerting selection for reduced pathogenesis when these bacteria inevitably evolve resistance to therapeutic intervention. As an example of such a management strategy, we isolated a lytic bacteriophage, OMKO1, (family Myoviridae) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that utilizes the outer membrane porin M (OprM) of the multidrug efflux systems MexAB and MexXY as a receptor-binding site. Results show that phage selection produces an evolutionary trade-off in MDR P. aeruginosa, whereby the evolution of bacterial resistance to phage attack changes the efflux pump mechanism, causing increased sensitivity to drugs from several antibiotic classes. Although modern phage therapy is still in its infancy, we conclude that phages, such as OMKO1, represent a new approach to phage therapy where bacteriophages exert selection for MDR bacteria to become increasingly sensitive to traditional antibiotics. This approach, using phages as targeted antibacterials, could extend the lifetime of our current antibiotics and potentially reduce the incidence of antibiotic resistant infections.
Related collections
Most cited references47
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found