- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ischemic Stroke and Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia following COVID-19 Vaccine: A Case Report with Systematic Review of the Literature
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) is a prothrombotic syndrome observed after adenoviral vector-based vaccines for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. It is characterized by thrombocytopenia, systemic activation of coagulation, extensive venous thrombosis, and anti-platelet factor 4 antibodies. Arterial thrombosis is less common and mainly affects the aorta, peripheral arteries, heart, and brain. Several cases of ischemic stroke have been reported in VITT, often associated with large vessel occlusion (LVO). Here, we describe a case of ischemic stroke with LVO after Ad26.COV2.S vaccine, then we systematically reviewed the published cases of ischemic stroke and VITT following COVID-19 vaccination.
Methods
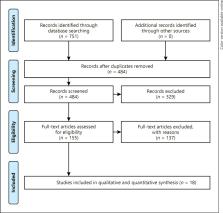
We describe a 58-year-old woman who developed a thrombotic thrombocytopenia syndrome with extensive splanchnic vein thrombosis and ischemic stroke due to right middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion, 13 days after receiving Ad26.COV2.S vaccination. Then, we performed a systematic review of the literature until December 3, 2021 using PubMed and EMBASE databases. The following keywords were used: (“COVID-19 vaccine”) AND (“stroke”), (“COVID-19 vaccine”) AND (“thrombotic thrombocytopenia”). We have selected all cases of ischemic stroke in VITT.
Results
Our study included 24 patients. The majority of the patients were females (79.2%) and younger than 60 years of age (median age 45.5 years). Almost all patients (96%) received the first dose of an adenoviral vector-based vaccine. Ischemic stroke was the presenting symptom in 18 patients (75%). Splanchnic venous thrombosis was found in 10 patients, and cerebral venous thrombosis in 5 patients (21%). Most patients (87.5%) had an anterior circulation stroke, mainly involving MCA. Seventeen patients (71%) had an intracranial LVO. We found a high prevalence of large intraluminal thrombi (7 patients) and free-floating thrombus (3 patients) in extracranial vessels, such as the carotid artery, in the absence of underlying atherosclerotic disease. Acute reperfusion therapy was performed in 7 of the 17 patients with LVO (41%). One patient with a normal platelet count underwent intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase, while 6 patients underwent mechanical thrombectomy. A malignant infarct occurred in 9 patients and decompressive hemicraniectomy was performed in 7 patients. Five patients died (21%).
Related collections
Most cited references76
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
