- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The psychological legacy of past obesity and early mortality: evidence from two longitudinal studies
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
We test a novel ‘weight scarring’ hypothesis which suggests that past obesity is associated with impairments in current psychological well-being and this increases risk of negative physical health outcomes associated with obesity. Across two nationally representative studies, we tested whether past obesity is associated with current psychological outcomes and whether these psychological outcomes explain the association between past obesity and subsequent early mortality.
Methods
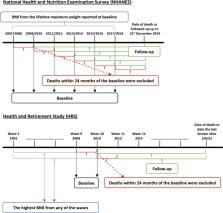
Data were from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) ( n = 29,047) and the Health and Retirement Study (HRS) ( n = 11,998). Past obesity was defined based on maximum lifetime weight in NHANES and the highest weight from past study waves in the HRS. Across both studies, current depressive symptoms were analysed. A set of 10 additional well-being measures were combined to produce an ‘index of impaired well-being’ in HRS. Subsequent all-cause mortality was examined using National Deaths Index records in NHANES and household interviews in HRS. Linear or logistic regression, Cox proportional hazard regression, and causal mediation models were used.
Results
We found that past obesity was associated with greater current depressive symptoms after controlling for current weight status and in analyses limited to those who were no longer classified as having obesity in NHANES ( β = 0.17; 95% CI: 0.13, 0.22) and HRS ( β = 0.20; 95% CI: 0.08, 0.31). In HRS, past obesity was also associated with a range of current negative psychological outcomes, including an index of impaired psychological well-being ( β = 0.16; 95% CI: 0.05, 0.27). Past obesity was associated with a higher risk of early mortality in both NHANES and HRS (HR = 1.31; 95% CI: 1.16, 1.48 and HR = 1.34; 95% CI: 1.20, 1.50, respectively). Depressive symptoms explained 6% (95% CI: 0.01, 0.10) and 5% (95% CI: 0.01, 0.09) of the association between past obesity and premature mortality in NHANES and HRS, respectively. Impaired psychological well-being partly mediated the association between past obesity and premature mortality by 10% (95% CI: 0.04, 0.16) in HRS.
Related collections
Most cited references82

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: a meta-analytic review.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found