- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Efficacy of neurodevelopmental treatment combined with the Nintendo ® Wii in patients with cerebral palsy
Read this article at
Abstract
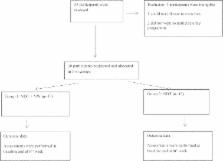
[Purpose] The aim of this study was to investigate the efficiency of Nintendo ® Wii games in addition to neurodevelopmental treatment in patients with cerebral palsy. [Subjects and Methods] Thirty hemiparetic cerebral palsy patients (16 females, 14 males; mean age, 6–15 years) were included in the study and divided into two groups: a neurodevelopmental treatment+Nintendo Wii group (group 1, n=15) and a neurodevelopmental treatment group (group 2, n=15). Both groups received treatment in 45-minute sessions 2 days/week for six weeks. Use of the upper extremities, speed, disability and functional independence were evaluated using the Quality of Upper Extremity Skills Test, Jebsen Taylor Hand Function Test, ABILHAND-Kids test, and Pediatric Functional Independence Measure (self-care) before and after treatment. [Results] There were statistically significant improvements in all parameters for group 1 and group 2 (except quality of function) after six weeks of treatment. Intergroup analysis showed that group 1 was superior to group 2 in mean change differences in the Jebsen Taylor Hand Function Test. [Conclusion] Our results showed that neurodevelopmental treatment is effective for improving hand functions in hemiplegic cerebral palsy. To provide a enjoyable, motivational, safe, and effective rehabilitation program, the Nintendo ® Wii may be used in addition to neurodevelopmental treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references19
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Surveillance of cerebral palsy in Europe: a collaboration of cerebral palsy surveys and registers. Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe (SCPE).
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Motor learning elicited by voluntary drive.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found