- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Heterogeneity in Colorectal Cancer: A Challenge for Personalized Medicine?
Read this article at
Abstract
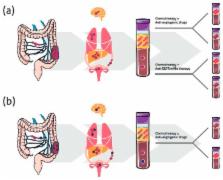
High inter-patient variability and high spatial heterogeneity are features of colorectal cancer (CRC). This may influence the molecular characterization of tumor tissue, now mandatory for patients with metastatic CRC who are candidates for treatment with an anti-EGFR mAb, as false-negative results can occur, leading to non optimal therapy. Moreover, temporal molecular heterogeneity during treatment is known to influence the response to therapy and prognosis. We present a literature overview of advances made in characterizing molecular heterogeneity in CRC, underlining that the analysis of liquid biopsy could represent an efficient non-invasive tool to overcome the problem. We believe that understanding CRC heterogeneity is fundamental for a more accurate diagnosis, for selecting the best targets to ensure prolonged antitumor response, and for monitoring minimal residual disease and the onset of resistance to therapy, all essential components of successful personalized treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references85
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical Sequencing Defines the Genomic Landscape of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Distal and proximal colon cancers differ in terms of molecular, pathological, and clinical features.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found