- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Regulation of Mammary Stem/Progenitor Cells by PTEN/Akt/β-Catenin Signaling
Read this article at
Abstract
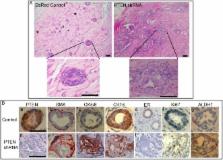
The PTEN/Akt/β-catenin pathway is important for maintaining stem or progenitor cells in normal and cancerous breast tissue and may be a promising target for effective, long-lasting cancer treatment.
Abstract
Recent evidence suggests that many malignancies, including breast cancer, are driven by a cellular subcomponent that displays stem cell-like properties. The protein phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is inactivated in a wide range of human cancers, an alteration that is associated with a poor prognosis. Because PTEN has been reported to play a role in the maintenance of embryonic and tissue-specific stem cells, we investigated the role of the PTEN/Akt pathway in the regulation of normal and malignant mammary stem/progenitor cell populations. We demonstrate that activation of this pathway, via PTEN knockdown, enriches for normal and malignant human mammary stem/progenitor cells in vitro and in vivo. Knockdown of PTEN in normal human mammary epithelial cells enriches for the stem/progenitor cell compartment, generating atypical hyperplastic lesions in humanized NOD/SCID mice. Akt-driven stem/progenitor cell enrichment is mediated by activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway through the phosphorylation of GSK3-β. In contrast to chemotherapy, the Akt inhibitor perifosine is able to target the tumorigenic cell population in breast tumor xenografts. These studies demonstrate an important role for the PTEN/PI3-K/Akt/β-catenin pathway in the regulation of normal and malignant stem/progenitor cell populations and suggest that agents that inhibit this pathway are able to effectively target tumorigenic breast cancer cells.
Author Summary
Healthy adult tissues are maintained through the regulated proliferation of a subset of cells known as tissue stem and progenitor cells. Many cancers, including breast cancer, also are thought to arise from and be maintained by a small population of cells that display stem cell-like properties. These so-called “cancer stem cells” may also contribute to tumor spread (metastasis), resistance to treatment, and disease relapse. Effective, long-lasting cancer treatments likely will need to target and eliminate these cancer stem cells specifically. Regulatory pathways responsible for maintaining cancer stem cells therefore may be promising targets for treatment. Breast cancers in humans frequently display abnormalities in the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. We demonstrate using cell culture and a mouse model of breast cancer that stem or progenitor cells in both normal breast tissue and breast tumors are dependent for their continued growth on this pathway and on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. We further show that the drug perifosine, which inhibits the kinase Akt, is able specifically to reduce the population of breast cancer stem or progenitor cells growing in mice. Our findings support the idea that drugs that selectively target breast cancer stem cells through the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway may reduce tumor growth and metastasis and result in improved patient outcomes.
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to chemotherapy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Breast cancer cell lines contain functional cancer stem cells with metastatic capacity and a distinct molecular signature.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
