- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The interplay of sex steroid hormones and microRNAs in endometrial cancer: current understanding and future directions
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
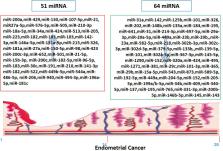
Endometrial cancer is a hormone-dependent malignancy, and sex steroid hormones play a crucial role in its pathogenesis. Recent studies have demonstrated that microRNAs (miRNAs) can regulate the expression of sex steroid hormone receptors and modulate hormone signaling pathways. Our aim is to provide an overview of the current understanding of the role of miRNAs in endometrial cancer regulated by sex steroid hormone pathways.
Methods
A thorough literature search was carried out in the PubMed database. The articles published from 2018 to the present were included. Keywords related to miRNAs, endometrial cancer, and sex steroid hormones were used in the search.
Results
Dysregulation of miRNAs has been linked to abnormal sex steroid hormone signaling and the development of endometrial cancer. Various miRNAs have been identified as modulators of estrogen and progesterone receptor expression, and the miRNA expression profile has been shown to be a predictor of response to hormone therapy. Additionally, specific miRNAs have been implicated in the regulation of genes involved in hormone-related signaling pathways, such as the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MAPK/ERK pathways.
Conclusion
The regulation of sex steroid hormones by miRNAs is a promising area of research in endometrial cancer. Future studies should focus on elucidating the functional roles of specific miRNAs in sex steroid hormone signaling and identifying novel miRNA targets for hormone therapy in endometrial cancer management.
Related collections
Most cited references204
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Loss of exosomal miR‐148b from cancer‐associated fibroblasts promotes endometrial cancer cell invasion and cancer metastasis

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found