- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
OR-methods for coping with the ripple effect in supply chains during COVID-19 pandemic: Managerial insights and research implications
Read this article at
Abstract
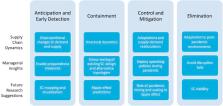
The COVID-19 pandemic unveils unforeseen and unprecedented fragilities in supply chains (SC). A primary stressor of SCs and their subsequent shocks derives from disruption propagation (i.e., the ripple effect) through related networks. In this paper, we conceptualize current state and future research directions on the ripple effect for pandemic context. We scrutinize the existing OR (Operational Research) studies published in international journals dealing with disruption propagation and structural dynamics in SCs. Our study pursues two major contributions in relation to two research questions. First, we collate state-of-the-art research on disruption propagation in SCs and identify a methodical taxonomy along with theories displaying their value and applications for coping with the impacts of pandemics on SCs. Second, we reveal and systemize managerial insights from theory used for operating (adapting) amid a pandemic and during times of recovery, along with becoming more resistant to future pandemics. Streamlining the literature allowed us to reveal several new research tensions and novel categorizations and classifications. The outcomes of our study show that methodical contributions and the resulting managerial insights can be categorized into three levels, i.e., network, process, and control. Our analysis reveals that adaptation capabilities play the most crucial role in managing the SCs under pandemic disruptions. Our findings depict how the existing OR methods can help coping with the ripple effect at five pandemic stages (i.e., Anticipation; Early Detection; Containment; Control and Mitigation; and Elimination) following the WHO classification. The outcomes and findings of our study can be used by industry and researchers alike to progress the decision-support systems guiding SCs amid the COVID-19 pandemic and toward recovery. Suggestions for future research directions are offered and discussed.
Related collections
Most cited references54
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Predicting the impacts of epidemic outbreaks on global supply chains: A simulation-based analysis on the coronavirus outbreak (COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2) case
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Viability of intertwined supply networks: extending the supply chain resilience angles towards survivability. A position paper motivated by COVID-19 outbreak
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
