- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
DNA Barcoding Evaluation and Its Taxonomic Implications in the Recently Evolved Genus Oberonia Lindl. (Orchidaceae) in China

Read this article at
Abstract
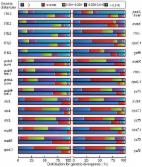
The orchid genus Oberonia Lindl., is a taxonomically complex genus characterized by recent species radiations and many closely related species. All Oberonia species are under conservation as listed in the CITES and the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria. Given its difficulties in taxonomy and conservation status, Oberonia is an excellent model for developing DNA barcodes. Three analytical methods and five DNA barcoding regions ( rbcL, matK, trnH-psbA, ITS, and ITS2) were evaluated on 127 individuals representing 40 species and 1 variety of Oberonia from China. All the three plastid candidates tested ( rbcL, matK, and trnH-psbA) have a lower discriminatory power than the nuclear regions (ITS and ITS2), and ITS had the highest resolution rate (82.14%). Two to four combinations of these gene sets were not better than the ITS alone, but when considering modes of inheritance, rbcL+ITS and matK+ITS were the best barcodes for identifying Oberonia species. Furthermore, the present barcoding system has many new insights in the current Oberonia taxonomy, such as correcting species identification, resolving taxonomic uncertainties, and the underlying presence of new or cryptic species in a genus with a complex speciation history.
Related collections
Most cited references46
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Validation of the ITS2 Region as a Novel DNA Barcode for Identifying Medicinal Plant Species
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.