- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Training of Manual Actions Improves Language Understanding of Semantically Related Action Sentences
Read this article at
Abstract
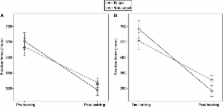
Conceptual knowledge accessed by language may involve the reactivation of the associated primary sensory-motor processes. Whether these embodied representations are indeed constitutive to conceptual knowledge is hotly debated, particularly since direct evidence that sensory-motor expertise can improve conceptual processing is scarce. In this study, we sought for this crucial piece of evidence, by training naive healthy subjects to perform complex manual actions and by measuring, before and after training, their performance in a semantic language task. Nineteen participants engaged in 3 weeks of motor training. Each participant was trained in three complex manual actions (e.g., origami). Before and after the training period, each subject underwent a series of manual dexterity tests and a semantic language task. The latter consisted of a sentence-picture semantic congruency judgment task, with 6 target congruent sentence-picture pairs (semantically related to the trained manual actions), 6 non-target congruent pairs (semantically unrelated), and 12 filler incongruent pairs. Manual action training induced a significant improvement in all manual dexterity tests, demonstrating the successful acquisition of sensory-motor expertise. In the semantic language task, the reaction times (RTs) to both target and non-target congruent sentence-picture pairs decreased after action training, indicating a more efficient conceptual-semantic processing. Noteworthy, the RTs for target pairs decreased more than those for non-target pairs, as indicated by the 2 × 2 interaction. These results were confirmed when controlling for the potential bias of increased frequency of use of target lexical items during manual training. The results of the present study suggest that sensory-motor expertise gained by training of specific manual actions can lead to an improvement of cognitive-linguistic skills related to the specific conceptual-semantic domain associated to the trained actions.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found