- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Occupational Exposure to Hexavalent Chromium, Nickel and PAHs: A Mixtures Risk Assessment Approach Based on Literature Exposure Data from European Countries
Read this article at
Abstract
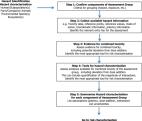
Hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)), nickel (Ni) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are genotoxic co-occurring lung carcinogens whose occupational health risk is still understudied. This study, conducted within the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU), aimed at performing a mixtures risk assessment (MRA) based on published human biomonitoring (HBM) data from Cr(VI), Ni and/or PAHs occupational co-exposure in Europe. After data extraction, Risk Quotient (RQ) and Sum of Risk Quotients (SRQ) were calculated for binary and ternary mixtures to characterise the risk. Most selected articles measured urinary levels of Cr and Ni and a SRQ > 1 was obtained for co-exposure levels in welding activities, showing that there is concern regarding co-exposure to these substances. Similarly, co-exposure to mixtures of Cr(VI), Ni and PAHs in waste incineration settings resulted in SRQ > 1. In some studies, a low risk was estimated based on the single substances’ exposure level (RQ < 1), but the mixture was considered of concern (SRQ > 1), highlighting the relevance of considering exposure to the mixture rather than to its single components. Overall, this study points out the need of using a MRA based on HBM data as a more realistic approach to assess and manage the risk at the workplace, in order to protect workers’ health.
Related collections
Most cited references65
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Guidance on harmonised methodologies for human health, animal health and ecological risk assessment of combined exposure to multiple chemicals
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found