- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Antimicrobial Resistance in Nepal
Read this article at
Abstract
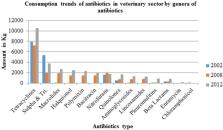
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a global problem to animal and public health. It has drawn the attention of public health experts, stakeholders, and medical science due to the substantial economic loss that it causes to individuals and nation as a whole. Various cross-sectional studies and some national surveys in developing countries have shown increase in the burden of antimicrobial resistance. Nepal is one of the major contributors to the growing burden of AMR due to widespread irrational use of antibiotics along with poor health care systems poor infection control and prevention measures. This review was conducted to summarize the situation of AMR in Nepal, determinants of AMR, current government intervention strategies and the way forward to reduce the AMR burden in Nepal. Available cross sectional reports warn that bacterial pathogens are becoming highly resistant to most first- and some second-line antibiotics. The irrational and injudicious use of high doses of antibiotics for therapy and sub-optimal doses as growth promoters are leading causes of AMR in Nepal. Establishment of a surveillance programme and a national plan for containment of AMR, following the National Antibiotics Treatment Guideline 2014 and generation of awareness among veterinarians, technicians, and medical physicians on prudent use of antimicrobial drugs in Nepal could reduce the burden of AMR. In addition, there is a need to develop a national laboratory strategic plan to provide guidance and governance to national laboratories.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Probiotics and prebiotics in animal feeding for safe food production.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Antibiotics in agriculture and the risk to human health: how worried should we be?

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found