- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Flexible and Waterproof 2D/1D/0D Construction of MXene-Based Nanocomposites for Electromagnetic Wave Absorption, EMI Shielding, and Photothermal Conversion

Read this article at
Abstract
Abstract
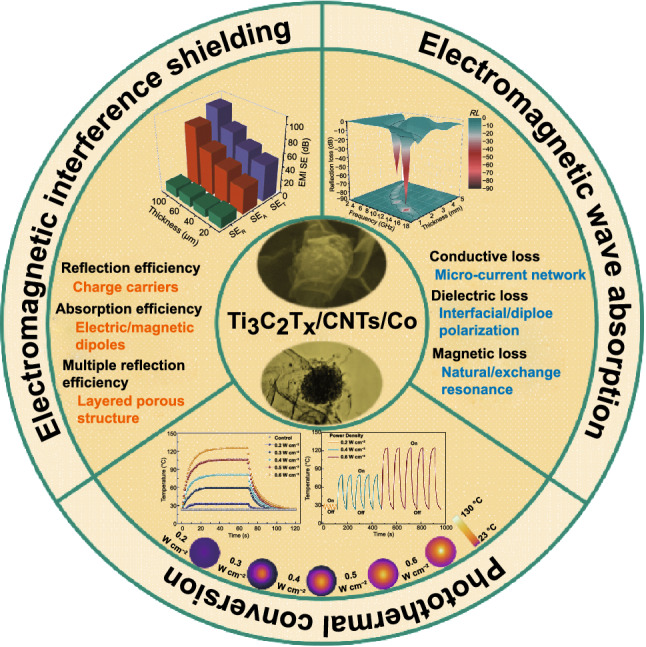
High-performance electromagnetic wave absorption and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials with multifunctional characters have attracted extensive scientific and technological interest, but they remain a huge challenge. Here, we reported an electrostatic assembly approach for fabricating 2D/1D/0D construction of Ti 3C 2T x/carbon nanotubes/Co nanoparticles (Ti 3C 2T x/CNTs/Co) nanocomposites with an excellent electromagnetic wave absorption, EMI shielding efficiency, flexibility, hydrophobicity, and photothermal conversion performance. As expected, a strong reflection loss of -85.8 dB and an ultrathin thickness of 1.4 mm were achieved. Meanwhile, the high EMI shielding efficiency reached 110.1 dB. The excellent electromagnetic wave absorption and shielding performances were originated from the charge carriers, electric/magnetic dipole polarization, interfacial polarization, natural resonance, and multiple internal reflections. Moreover, a thin layer of polydimethylsiloxane rendered the hydrophilic hierarchical Ti 3C 2T x/CNTs/Co hydrophobic, which can prevent the degradation/oxidation of the MXene in high humidity condition. Interestingly, the Ti 3C 2T x/CNTs/Co film exhibited a remarkable photothermal conversion performance with high thermal cycle stability and tenability. Thus, the multifunctional Ti 3C 2T x/CNTs/Co nanocomposites possessing a unique blend of outstanding electromagnetic wave absorption and EMI shielding, light-driven heating performance, and flexible water-resistant features were highly promising for the next-generation intelligent electromagnetic attenuation system.
Highlights
-
The 2D/1D/0D Ti 3C 2T x/carbon nanotubes/Co nanocomposite is successfully synthesized via an electrostatic assembly.
-
Nanocomposites exhibit an excellent electromagnetic wave absorption and a remarkable electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency.
-
The flexible, waterproof, and photothermal conversion performances are achieved.
Related collections
Most cited references115
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide 'clay' with high volumetric capacitance.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes)
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Synthesis of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): routes to various MOF topologies, morphologies, and composites.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
