- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Antioxidant and Antiacetylcholinesterase Activities of Some Commercial Essential Oils and Their Major Compounds
Read this article at
Abstract
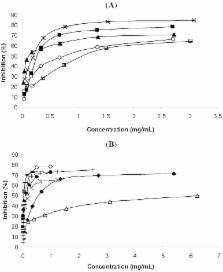
The commercial essential oils of Citrus aurantium L., Cupressus sempervirens L., Eucalyptus globulus Labill., Foeniculum vulgare Mill. and Thymus vulgaris L., isolated by steam distillation by a company of Morocco were evaluated in terms of in vitro antioxidant activity through several methods. In vitro acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity was also determined. Citrus limon (L.) Burm. f. oil was also studied, but it was obtained by peel expression. The best antioxidant was T. vulgaris oil, independent of the method used, mainly due to the presence of the phenolic monoterpenes thymol and carvacrol, which when studied as single compounds also presented the best activities. Concerning the acetylcholinesterase inhibition activity, E. globulus was the most effective. Nevertheless its main components 1,8-cineole and limonene were not the most active, a feature that corresponded to δ-3-carene.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Malondialdehyde and thiobarbituric acid-reactivity as diagnostic indices of lipid peroxidation and peroxidative tissue injury.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Essential Oils: A Short Review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found