- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Age- and Brain Region-Specific Changes of Glucose Metabolic Disorder, Learning, and Memory Dysfunction in Early Alzheimer’s Disease Assessed in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice Using 18F-FDG-PET
Read this article at
Abstract
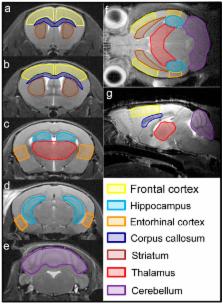
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a leading cause of dementia worldwide, associated with cognitive deficits and brain glucose metabolic alteration. However, the associations of glucose metabolic changes with cognitive dysfunction are less detailed. Here, we examined the brains of APP/presenilin 1 (PS1) transgenic (Tg) mice aged 2, 3.5, 5 and 8 months using 18F-labed fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18F-FDG) microPET to assess age- and brain region-specific changes of glucose metabolism. FDG uptake was calculated as a relative standardized uptake value (SUVr). Morris water maze (MWM) was used to evaluate learning and memory dysfunction. We showed a glucose utilization increase in multiple brain regions of Tg mice at 2 and 3.5 months but not at 5 and 8 months. Comparisons of SUVrs within brains showed higher glucose utilization than controls in the entorhinal cortex, hippocampus, and frontal cortex of Tg mice at 2 and 3.5 months but in the thalamus and striatum at 3.5, 5 and 8 months. By comparing SUVrs in the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus, Tg mice were distinguished from controls at 2 and 3.5 months. In MWM, Tg mice aged 2 months shared a similar performance to the controls (prodromal-AD). By contrast, Tg mice failed training tests at 3.5 months but failed all MWM tests at 5 and 8 months, suggestive of partial or complete cognitive deficits (symptomatic-AD). Correlation analyses showed that hippocampal SUVrs were significantly correlated with MWM parameters in the symptomatic-AD stage. These data suggest that glucose metabolic disorder occurs before onset of AD signs in APP/PS1 mice with the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus affected first, and that regional FDG uptake increase can be an early biomarker for AD. Furthermore, hippocampal FDG uptake is a possible indicator for progression of Alzheimer’s cognition after cognitive decline, at least in animals.
Related collections
Most cited references34
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Discrimination between Alzheimer dementia and controls by automated analysis of multicenter FDG PET.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Comparing positron emission tomography imaging and cerebrospinal fluid measurements of β-amyloid.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found