- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Leptospirosis in Germany, 1962–2003

Read this article at
Abstract
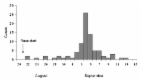
Epidemiologic trends of human leptospirosis in Germany were investigated by analyzing national surveillance data from 1962 to 2003 and by conducting a questionnaire-based survey from 1997 to 2000. After a steady decrease of leptospirosis incidence from 1962 to 1997, surveillance data indicate an increase in disease incidence to 0.06 per 100,000 (1998–2003). Of 102 laboratory-confirmed cases in humans from 1997 to 2000, 30% were related to occupational exposures. Recreational exposures were reported in 30% (including traveling abroad in 16%), whereas residential exposure accounted for 37% of the cases. Direct contact with animals, mostly rats and dogs, was observed in 31% of the cases. We conclude that recent changes in transmission patterns of leptospirosis, partially caused by an expanding rat population and the resurgence of canine leptospirosis, may facilitate the spread of the disease in temperate countries like Germany. Preventive measures should be adapted to the changing epidemiology of leptospirosis.
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Usefulness of serologic analysis as a predictor of the infecting serovar in patients with severe leptospirosis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found