- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Preparation of a nanopearl powder/C-HA (chitosan-hyaluronic acid)/rhBMP-2 (recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2) composite artificial bone material and a preliminary study of its effects on MC3T3-E1 cells
Read this article at
ABSTRACT
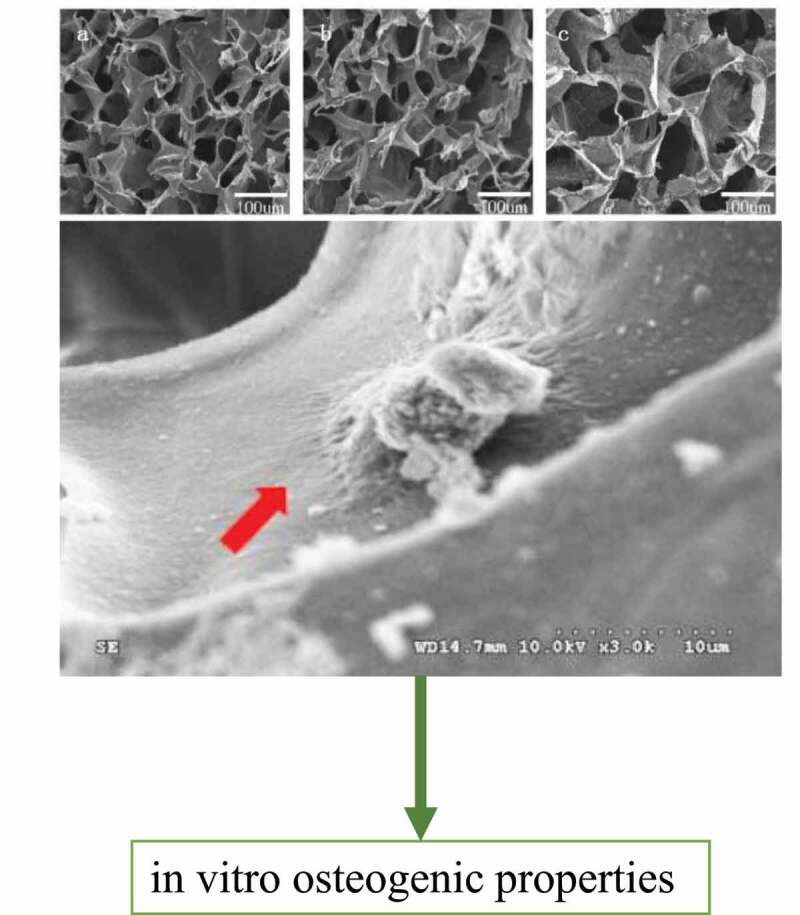
A nanopearl powder/C-HA (chitosan-hyaluronic acid)/rhBMP-2 (recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2) composite artificial bone material was prepared, and its biological properties were evaluated. The nanopearl powder/C-HA/rhBMP-2 composite porous artificial bone material was prepared using the freeze-drying method after the nanopearl powder was prepared using mechanical ball milling. The particle was measured with a transmission electron microscope, its surface morphology and pore size were observed under a scanning electron microscope. The porosity of the artificial bone was determined using pycnometry, a compression performance test was conducted with a universal testing machine, and XRD (X-ray diffraction) patterns were recorded to examine the crystal form of the pearl powder in the composite artificial bone. Finally, the artificial bone was cocultured with mouse MC3T3-E1 cells to investigate its effects on cell proliferation and differentiation and the expression of osteogenesis-related genes. The pearl powder prepared in this experiment had a particle size in the nanometer range. This nanopearl powder, along with C-HA and rhBMP-2, was compounded into the nanopearl powder/C-HA/rhBMP-2 composite artificial bone, showing pore sizes of 188.53 ± 15.32 μm, a porosity of 86.43 ± 2.78% and a compressive strength of 0.342 ± 0.024 MPa. Notably, rhBMP-2 was released from the artificial bone in a sustained manner. Moreover, this artificial bone promoted the adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells and upregulated the expression of ColαI (collagen α1), OCN (osteocalcin), OPN (osteopontin) and Runx2 (runt-related gene 2). Conclusively, this nanopearl powder/C-HA/rhBMP-2 composite artificial bone material showed good performance and cytocompatibility, suggesting that it can be used for bone tissue engineering.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The effect of mean pore size on cell attachment, proliferation and migration in collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Effect of pore size and void fraction on cellular adhesion, proliferation, and matrix deposition.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.