- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Population screening for colorectal cancer by flexible sigmoidoscopy or CT colonography: study protocol for a multicenter randomized trial
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second most prevalent type of cancer in Europe. A single flexible sigmoidoscopy (FS) screening at around the age of 60 years prevents about one-third of CRC cases. However, FS screens only the distal colon, and thus mortality from proximal CRC is unaffected. Computed tomography colonography (CTC) is a highly accurate examination that allows assessment of the entire colon. However, the benefit of CTC testing as a CRC screening test is uncertain. We designed a randomized trial to compare participation rate, detection rates, and costs between CTC (with computer-aided detection) and FS as primary tests for population-based screening.
Methods/Design
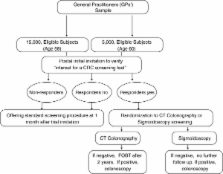
An invitation letter to participate in a randomized screening trial comparing CTC versus FS will be mailed to a sample of 20,000 people aged 58 or 60 years, living in the Piedmont region and the Verona district of Italy. Individuals with a history of CRC, adenomas, inflammatory bowel disease, or recent colonoscopy, or with two first-degree relatives with CRC will be excluded from the study by their general practitioners. Individuals responding positively to the invitation letter will be then randomized to the intervention group (CTC) or control group (FS), and scheduled for the screening procedure. The primary outcome parameter of this part of the trial is the difference in advanced neoplasia detection between the two screening tests. Secondary outcomes are cost-effectiveness analysis, referral rates for colonoscopy induced by CTC versus FS, and the expected and perceived burden of the procedures. To compare participation rates for CTC versus FS, 2,000 additional eligible subjects will be randomly assigned to receive an invitation for screening with CTC or FS. In the CTC arm, non-responders will be offered fecal occult blood test (FOBT) as alternative screening test, while in the FS arm, non-responders will receive an invitation letter to undergo screening with either FOBT or CTC. Data on reasons for participation and non-participation will also be collected.
Related collections
Most cited references44
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Reducing mortality from colorectal cancer by screening for fecal occult blood. Minnesota Colon Cancer Control Study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found