- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Altered Resting-State Functional Activity in Patients With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Quantitative Meta-Analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
Background: There is accumulating evidence showing that patients with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) have obvious changes in resting-state functional brain activity. So far, there have been no meta-analyses of the resting-state brain activity alterations in patients with ASD. We attempted to explore the resting-state functional activity changes in patients with ASD, possibly providing a new perspective for investigating the pathophysiology of patients with ASD.
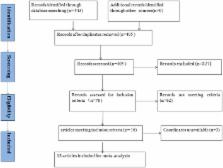
Methods: We screened relevant studies published before August 2017 in PubMed, Ovid, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and the Wan-fang database. Fifteen resting-state functional neural activity datasets (including 382 patients and 348 healthy controls) were included. Through the use of the effect-size signed differential mapping (ES-SDM) method, we carried out a meta-analysis of resting-state functional activity studies of patients with ASD.
Results: Compared with healthy controls, patients with ASD showed hyperactivity in the right supplementary motor area, middle frontal gyrus, inferior frontal gyrus, the left precentral gyrus, and the bilateral cerebellum hemispheric lobule (VIII/IX), and hypoactivity in the right middle temporal gyrus, superior temporal gyrus, and the left precuneus, posterior cingulate cortex, median cingulate cortex, and bilateral cerebellum (crus I).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis indicates that patients with ASD have significant and robust resting-state brain activity alterations in the language comprehension network, inferior-posterior cerebellum, default mode network (DMN), and cerebellar crus I. These brain regions may serve as specific regions of interest for further studies of ASD, which will allow us to further clarify the neurobiological mechanisms in patients with ASD.
Related collections
Most cited references34
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cortical activation and synchronization during sentence comprehension in high-functioning autism: evidence of underconnectivity.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Voxel-wise meta-analysis of grey matter changes in obsessive-compulsive disorder.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found